Evolving Landscape of Mitochondrial Disease Market: Key Insights of Latest Published Report—Leigh Syndrome, Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy, MELAS Syndrome, and Thymidine Kinase 2 Deficiency | DelveInsight
The mitochondrial disease market is witnessing steady growth, driven by increasing awareness, improved genetic diagnostics, and advancements in personalized medicine. Rising prevalence of mitochondrial disorders and supportive government funding for rare disease research are also fueling market expansion.
New York, USA, May 26, 2025 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Evolving Landscape of Mitochondrial Disease Market: Key Insights of Latest Published Report—Leigh Syndrome, Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy, MELAS Syndrome, and Thymidine Kinase 2 Deficiency | DelveInsight
The mitochondrial disease market is witnessing steady growth, driven by increasing awareness, improved genetic diagnostics, and advancements in personalized medicine. Rising prevalence of mitochondrial disorders and supportive government funding for rare disease research are also fueling market expansion.
Mitochondrial disease refers to a group of rare, often debilitating genetic disorders caused by dysfunctional mitochondria—the energy-producing structures within cells. Since mitochondria are responsible for generating the majority of a cell’s energy, their impairment can affect multiple organ systems, especially those with high energy demands, such as the brain, muscles, heart, and liver. These diseases can be inherited through nuclear DNA or mitochondrial DNA, and symptoms vary widely depending on which organs are affected. Common manifestations include muscle weakness, seizures, developmental delays, vision and hearing loss, and fatigue. There is currently no cure, and treatment is generally supportive, aimed at managing symptoms and slowing disease progression.
The patient burden of mitochondrial disease is significant. Many individuals face a lifetime of complex symptoms requiring frequent medical care and multi-specialty coordination. The disease often leads to progressive loss of function, severely limiting daily activities and quality of life. Caregivers also experience high levels of emotional and financial stress due to the unpredictable nature of the illness and lack of effective therapies. Globally, mitochondrial diseases are estimated to affect about 1 in 5,000 individuals, but they remain underdiagnosed and misunderstood. The burden is compounded by diagnostic delays and limited access to specialized care, highlighting the urgent need for increased awareness, research funding, and development of targeted treatments.
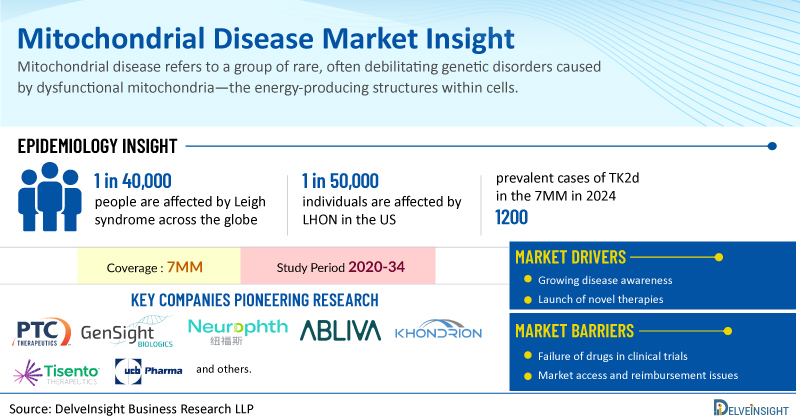
DelveInsight has expertise in the mitochondrial disease market, and an experienced team handles this domain proficiently. DelveInsight has recently released a series of epidemiology-based market reports on different types of mitochondrial diseases, including Leigh Syndrome, Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy, MELAS Syndrome, and Thymidine Kinase 2 Deficiency. These reports include a comprehensive understanding of current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted market size from 2020 to 2034, segmented into 7MM [the United States, the EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan].
Additionally, the reports feature an examination of prominent companies working with their lead candidates in different stages of clinical development. Let’s dive deeply into the market assessment of these mitochondrial disease types individually.
Leigh syndrome, also called subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy, is a rare, serious genetic neurometabolic condition that falls under primary mitochondrial disorders. It stems from disruptions in the body’s ability to produce energy at the cellular level, causing the progressive deterioration of the central nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves.
More than 75 genes have been associated with Leigh syndrome, most of which are involved in cellular energy metabolism. However, because many cases still lack a confirmed genetic diagnosis, this list is likely incomplete. Although some acquired conditions can resemble Leigh syndrome, a confirmed diagnosis requires clear evidence of a mitochondrial disorder. The condition affects an estimated 1 in 40,000 people.
Currently, there is no approved cure for Leigh syndrome. Treatment is primarily supportive, aimed at relieving symptoms, slowing progression, and improving quality of life. A key aspect of management involves addressing lactic acidosis, a hallmark feature that contributes to fatigue, muscle weakness, and breathing issues. Nutritional support is also critical, often requiring gastrostomy tube (G-tube) feeding in children with difficulty eating or increased caloric demands due to metabolic stress.
While most patients rely on symptomatic care, some individuals with specific genetic mutations may benefit from targeted therapies. For instance, those with mutations in the SLC19A3 gene, associated with biotin-thiamine-responsive basal ganglia disease, may respond to high doses of thiamine and biotin. Similarly, individuals with biotinidase deficiency caused by BTD mutations can be treated effectively with biotin supplementation. In pyruvate dehydrogenase complex deficiency, a ketogenic diet (high-fat, low-carb) along with thiamine has shown promise.
Despite these advances, the therapeutic pipeline for Leigh syndrome remains sparse, with only a few companies actively working on treatments. One such company, PTC Therapeutics, is developing Vatiquinone as a potential option.
Leigh syndrome represents a significant unmet medical need due to its rapid neurodegeneration, complex genetics, and lack of curative therapies. Patients often present with early-onset symptoms such as developmental regression, seizures, and respiratory issues, leading to poor survival outcomes. The genetic and clinical variability of the disease complicates both diagnosis and personalized treatment strategies. Its multisystem nature necessitates coordinated, multidisciplinary care, which is often inconsistent. There is an urgent need for effective treatments, improved diagnostic tools, and integrated care models to better support affected individuals and families.
According to DelveInsight, the market for Leigh syndrome is expected to grow between 2025 and 2034, driven by the emergence of new therapies and increasing global healthcare investment.
Discover more about the Leigh syndrome market in detail @ Leigh Syndrome Market Report
Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Market
Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) is typically linked to specific mitochondrial DNA mutations, notably G11778A, T14484C, and G3460A. These mutations primarily impact genes involved in mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I, including ND1, ND4, and ND6.
Given its rarity in the U.S. (affecting roughly 1 in 50,000 individuals), LHON is frequently underdiagnosed, misinterpreted, or improperly treated, which can worsen the condition. Vision loss associated with LHON predominantly affects males (70% to 90% of cases), typically emerging between the ages of 20 and 30. In females, the onset tends to occur later in life.
Currently, there is no definitive cure for LHON. Antioxidants are sometimes used to reduce oxidative stress from reactive oxygen species. Supplements such as vitamins B12 and C, Coenzyme Q10, brimonidine, and lutein have shown minimal benefit but may be recommended. Patients are encouraged to avoid neurotoxic substances like alcohol and tobacco, which can aggravate mitochondrial dysfunction.
Various "mitochondrial cocktail" therapies have been investigated for treating mitochondrial disorders such as LHON. These formulations may include ingredients like Coenzyme Q10, L-carnitine, creatine, lipoic acid, dimethylglycine, cysteine, succinate, dichloroacetate, and several vitamins (K1, K3, C, B1, B2, and E). However, current evidence does not strongly support their effectiveness for LHON treatment.
Idebenone, marketed under the brand name RAXONE, is an approved treatment for visual impairment in LHON patients and received EMA approval in 2015. Several investigational therapies are in development, including LUMEVOQ (GS010) by GenSight Biologics, NR082 (NFS-01) by Neurophth Therapeutics, and NV354 by Abliva.
In March 2025, GenSight Biologics shared updated scientific findings on LUMEVOQ at the 51st Annual NANOS Meeting. From 2025 to 2034, the LHON treatment market is expected to grow, driven by increased prevalence, better diagnostic practices, therapeutic advancements, an aging population, greater disease awareness, and favorable regulatory support across the 7MM.
For a comprehensive view of the LHON market, check out the Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy Market Assessment
Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) is a mitochondrial disease that mainly affects the brain and muscles. It typically appears in childhood or early adulthood, presenting with recurring episodes of encephalopathy, muscle weakness, headaches, and localized neurological impairments.
MELAS is caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA, which is inherited exclusively from the mother, as mtDNA from the father's sperm is usually eliminated during fertilization. As a result, an affected mother can pass the mutation to all her children, but only her daughters can continue passing it on to future generations.
Among the mutations linked to MELAS, the m.3243A>G variant in the MTTL1 gene is the most common. This is due to its relatively high mutation rate and its disruptive effect on essential mitochondrial functions. Its prominence in diagnostic testing also contributes to its frequent detection.
Currently, there are no approved treatments specifically for MELAS, highlighting a critical unmet medical need. To manage seizures, anticonvulsants are commonly prescribed; however, valproate has been reported in some cases to worsen MELAS-related epilepsy, though the underlying mechanism remains unclear. In many instances, delays in genetic confirmation of the disease complicate timely diagnosis and treatment, further affecting patients' quality of life.
L-arginine has been shown to lessen the severity and frequency of acute episodes, while L-citrulline may reduce stroke risk and aid in recovery. Both compounds are precursors to nitric oxide, and their benefits are thought to come from correcting nitric oxide deficiency often seen in MELAS patients. For those experiencing hearing loss, cochlear implants can help restore some hearing capacity.
The experimental drug idebenone has been tested for one month in individuals with MELAS carrying the m.3243A>G mutation. Clinical trials aim to evaluate whether idebenone can reduce brain lactate levels, as measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), and assess its safety and tolerability.
Various metabolic therapies and dietary supplements have shown promise in supporting mitochondrial function and slowing disease progression. These include carnitine, coenzyme Q10, idebenone, thiamine, riboflavin, creatine monohydrate, succinate, and others. While individual benefits have been observed, more research is needed to confirm their overall effectiveness.
Several pharmaceutical companies are actively pursuing new treatment options. Notable candidates under development include Sonlicromanol by Khondrion, Zagociguat by Tisento Therapeutics, and KL1333 by Abliva. According to DelveInsight, the MELAS syndrome market across the 7MM is expected to grow between 2025 and 2034, driven by innovative drug development, improved diagnostics, and increased disease awareness.
Looking for detailed MELAS syndrome market insights? Check out our latest MELAS Syndrome Market Assessment
Thymidine Kinase 2 Deficiency Market
Thymidine Kinase 2 deficiency (TK2d) is a rare and life-threatening genetic disorder that mainly affects mitochondrial function. It stems from mutations in the TK2 gene, which is essential for replicating mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA). These mutations lead to mtDNA depletion, resulting in severe muscle weakness and widespread systemic complications.
According to DelveInsight's analysis, there were nearly 1,200 prevalent TK2d cases across the 7MM (US, EU5, and Japan) in 2024, with numbers expected to rise during 2025–2034 due to improvements in genetic diagnostics and greater access to healthcare.
Currently, there are no approved therapies specifically targeting TK2d. Treatment primarily focuses on symptom management through a multidisciplinary care model. This approach is vital for enhancing the quality of life and minimizing complications. Neurological care is especially important, with physical and occupational therapies aimed at slowing muscle degeneration, maintaining mobility, and supporting independence. As the disease advances, respiratory failure becomes a major concern, and many patients require either non-invasive or invasive ventilation to maintain proper oxygenation and reduce the risk of respiratory complications, an essential step to extend survival.
Nutritional care is another critical component, as TK2d patients frequently struggle with swallowing, fatigue, and muscle weakness, putting them at high risk for malnutrition. High-calorie diets are typically prescribed, and in more severe cases, gastrostomy feeding is necessary to ensure adequate nutrition. Mobility aids, such as wheelchairs and assistive devices, are often required as the condition worsens, helping to preserve autonomy and alleviate physical limitations. While supportive care is indispensable, the absence of disease-modifying therapies highlights a significant unmet need for treatments that address the root cause of TK2d.
The TK2d drug development pipeline is limited, with few therapies in clinical stages. Among the most promising is MT1621 (developed by UCB Pharma), which is expected to be approved in the near future. Its launch is projected to fill a critical treatment gap and significantly enhance patient outcomes.
In March 2025, UCB shared encouraging results for its investigational therapy, doxecitine and doxribtimine, at the MDA Conference. The treatment demonstrated marked improvements in survival and functional performance, particularly in patients with early-onset symptoms. Data were collected from clinical trials and an expanded access program. While currently under regulatory review in both the US and EU, the therapy has not yet received formal approval.
The estimated TK2d market size in the 7MM was around USD 1 million in 2024, and it is expected to grow significantly over the forecast period. This growth will be driven by rising disease prevalence, increased awareness of genetic testing, and the introduction of new therapies.
Discover more about TK2D drugs in development @ Thymidine Kinase 2 Deficiency Clinical Trials
About DelveInsight
DelveInsight is a leading Business Consultant and Market Research firm focused exclusively on life sciences. It supports pharma companies by providing comprehensive end-to-end solutions to improve their performance. Get hassle-free access to all the healthcare and pharma market research reports through our subscription-based platform PharmDelve.

Contact Us Shruti Thakur info@delveinsight.com +14699457679 www.delveinsight.com
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.
